
Summary
1. Binding Condition might obviate the need for constraints like Tensed S Condi-
tion
and Specified Subject Condition.
(a) *Mary thinks that herself will win (TSC) -> violates BC (A)
(b) *Mary2 wants [S John to help herself2] (SSC) -> violates BC(A)
2. Subjacency Condition obviates Complex Noun Phrase Constraint, Sentential
Subject
Constraint and WH-Island Constraint.
(a) *Who are you reading a book that criticizes ? (p.232)
(b) *What would for me to do annoy you? (p. 233)
(c) *What might he ask whether I hid ? (p. 234)
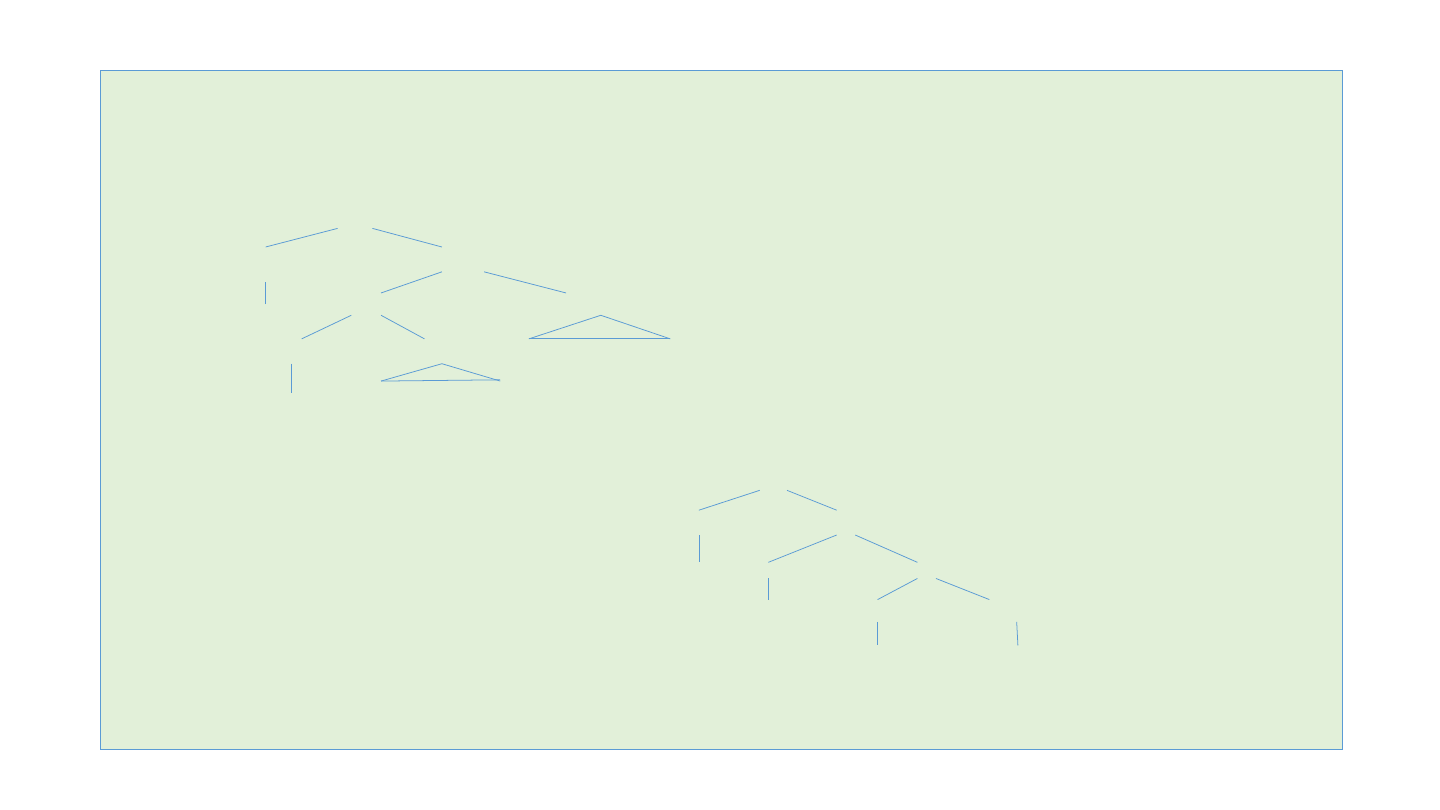

3. Complement and Adjunct
(1) a student of physics at Cambridge
NP
DET N’
a N’ PP
N PP at Cambridge
student of physics
(a) a Cambridge physics student
NP
(b) *a physics Cambridge student
DET N’
a NP N’
Cambridge NP N
physics student
(2) (a) He will work [at the job] (complement)
(b) He will work [at the office] (adjunct)
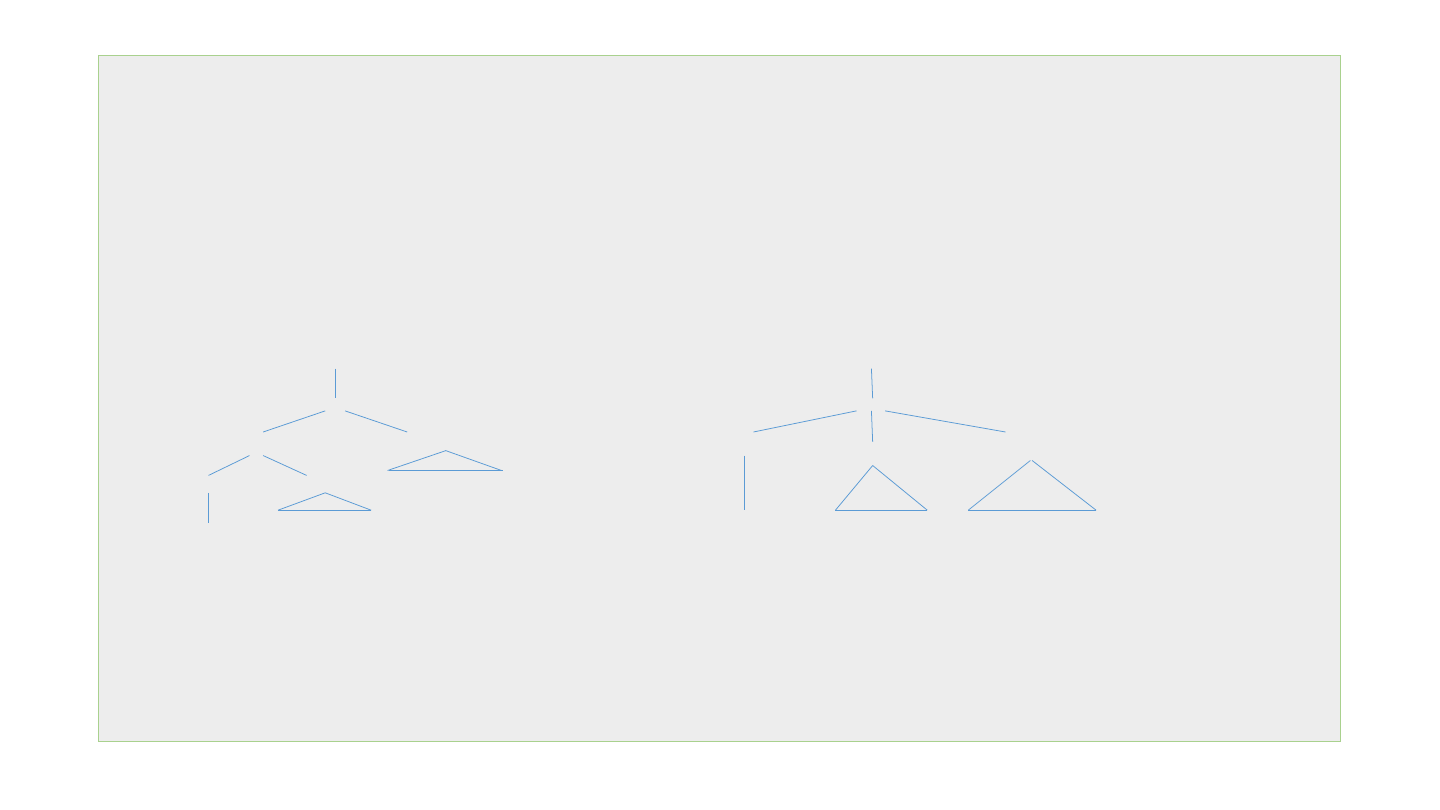
(3) (a) John will buy [NP the book] [PP on Tuesday]
(b) John will put [NP the book] [PP on the table]
VP VP
V’ V’
V’ PP V NP PP
V NP on Tuesday
buy the book put the book on the table
4. Structural Ambiguity
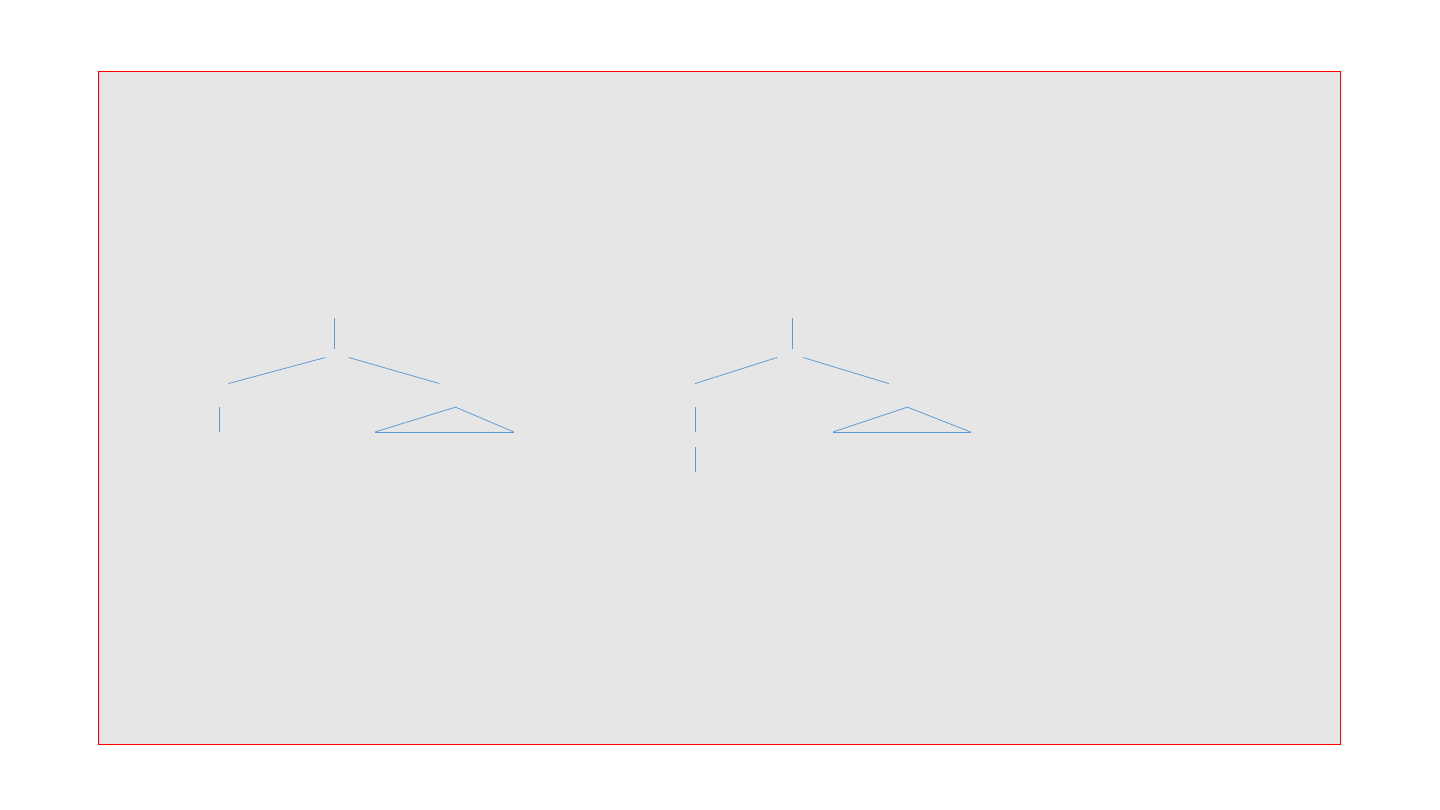
(1) He may decide [PP on the boat]
(2) He couldn’t explain [NP last night]
VP VP
V’ V’
V PP V’ PP
decide on the boat V on the boat
decide
# Structural Ambiguity can be determined by semantic interpretation of PP or NP.