
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Robot Learning:
Reinforcement Learning
Lecture 9
양정연
2020/12/10
1
T&C LAB-AI
Process Learning
(Sequence Learning)
1
2
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
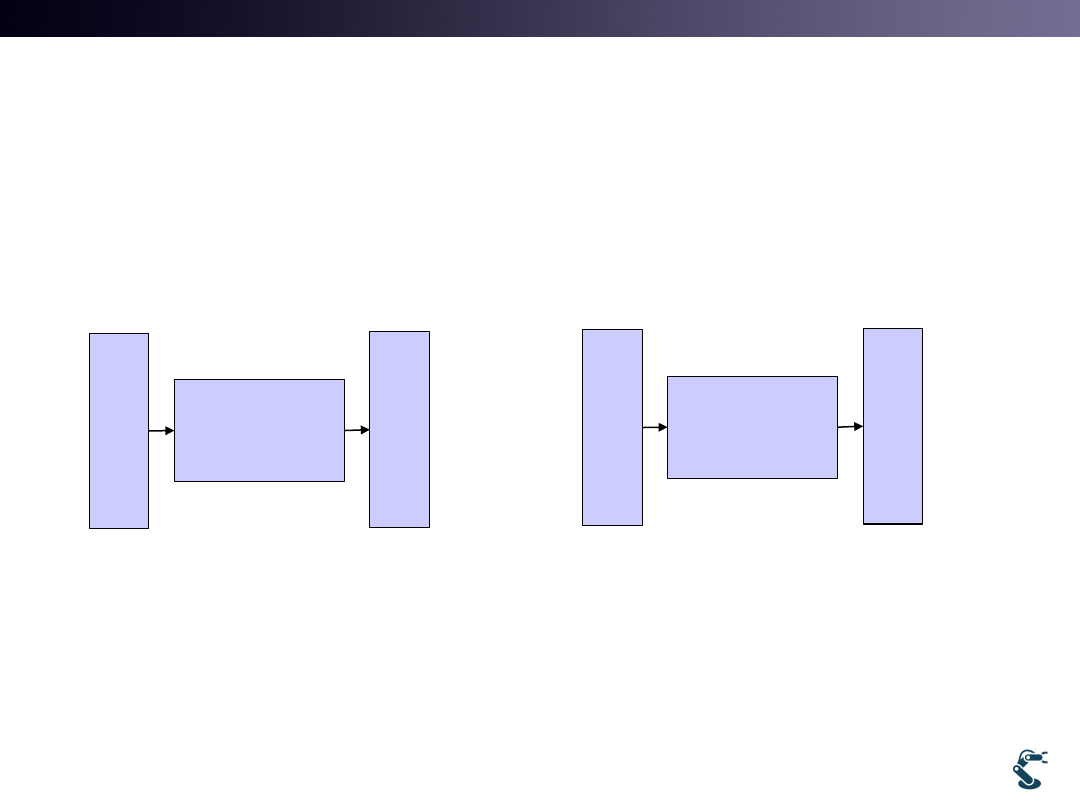
1. What learning methods try to learn?
• Think about Neural Network and Linear Regression
• Is it True?
3
Neural
Network
x
y
Data (x, y) are given
Goal is to find the proper
function, NN
2
1 )
(
(
)
w
y
f x
w x
Learning the function!
Linear
Regression
x
y
Data (x, y) are given
Goal is to find the proper
function, y=ax+b
Learning
method
( )
y
f x
Learning the function!
Linear Regression is Equal to Basic NN
wx
Nonlinear Kernels works for creating Hyperplane.
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
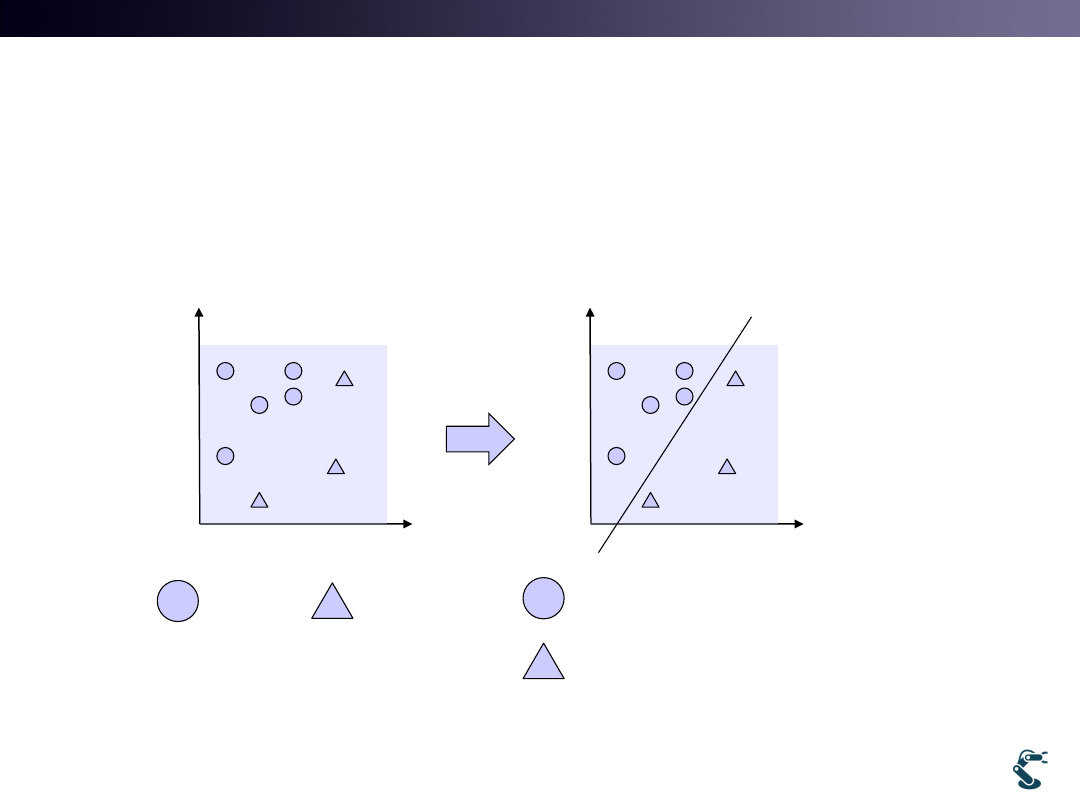
Definition of Hyperplane
• Hyperplane is a subspace that
– reduces the dimensionality of an original space.
– 2 Dim. Space is projected on a New Space with y=wx.
4
x
y
x
y
y=wx
2
R
2
R
{ , |
}
x y y
wx
{ , |
}
x y y
wx
Linear
Transformation
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
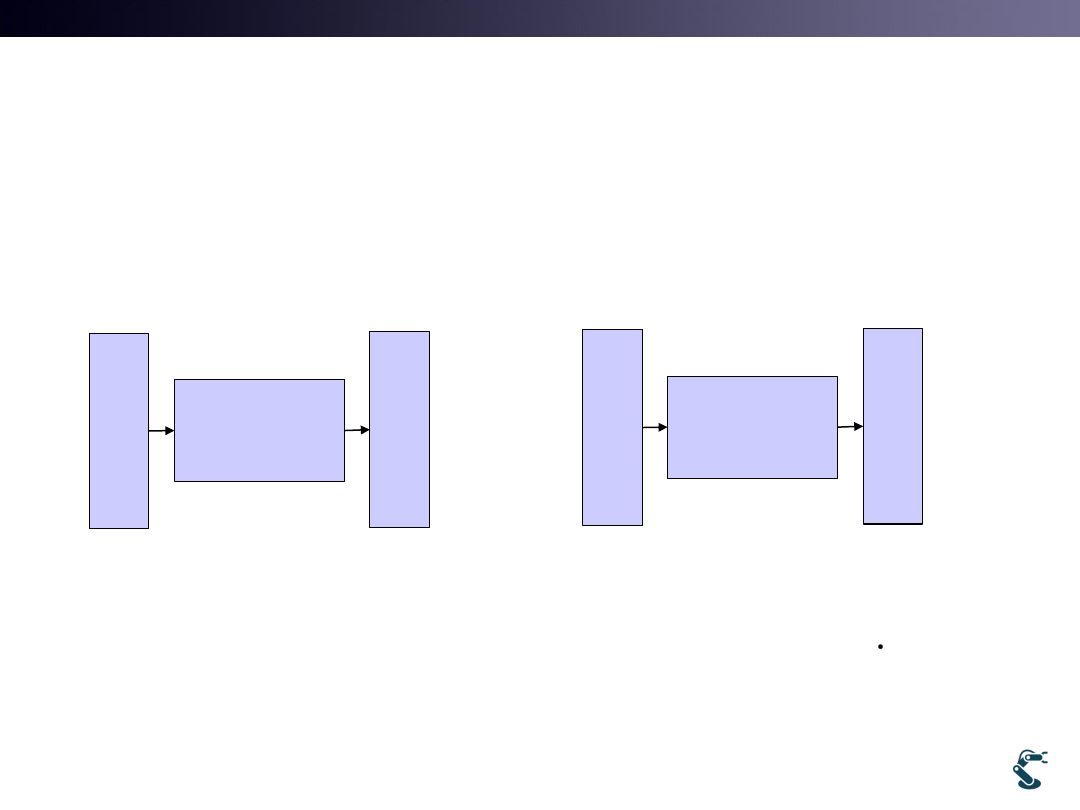
2. What learning method try to learn?
• Think about Neural Network and Control
• Control is the Modeling based Method.
5
Neural
Network
x
y
Data (x, y) are given
Goal is to find the proper
function, NN
( )
y
f x
Learning the function!
Math. Model
PD control
e
T
p
d
T
K e K e
Error, e is given and we
design a controller,
Design or Model a function
Learning
method
We don’t
care
about the
output, T
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
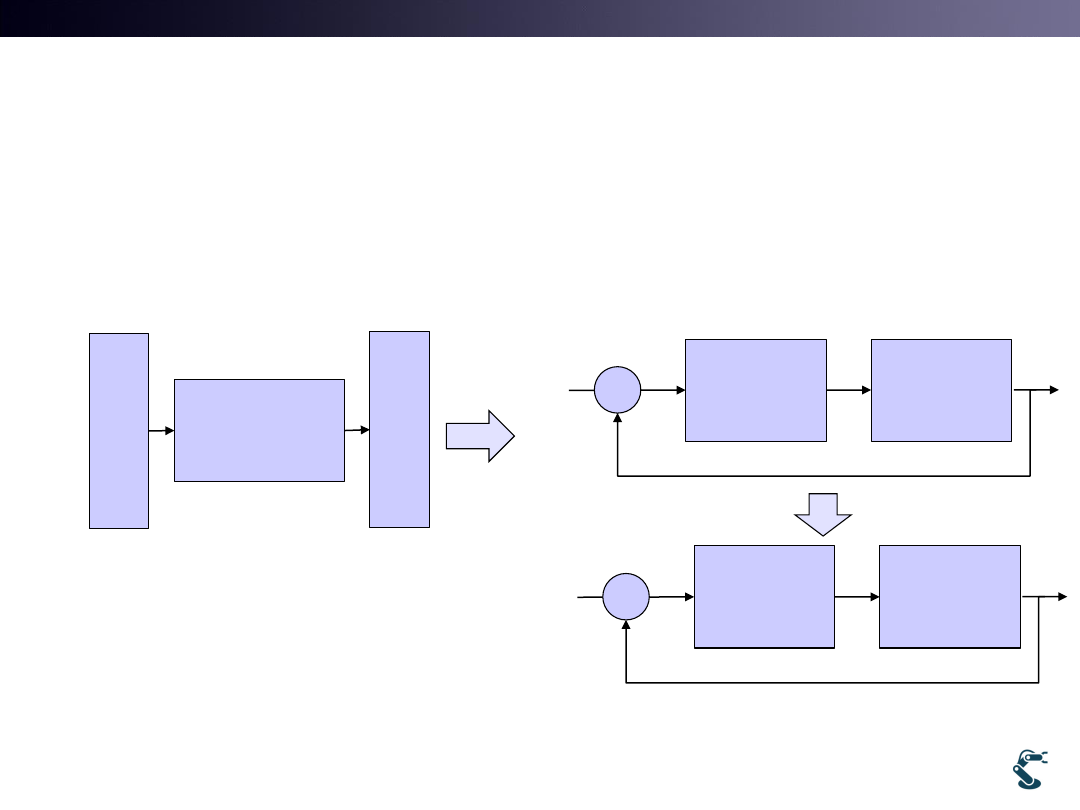
3. If we use NN in the control,
What happens?
• Think Control Diagram
• Input and output are different in every time Failed
6
Neural
Network
x
y
Data (x, y) are given
Goal is to find the proper
function, NN
( )
y
f x
Learning the function!
Learning
method
controller
System
xd
e
T
NN
System
xd
e
T
(e)
T
f
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
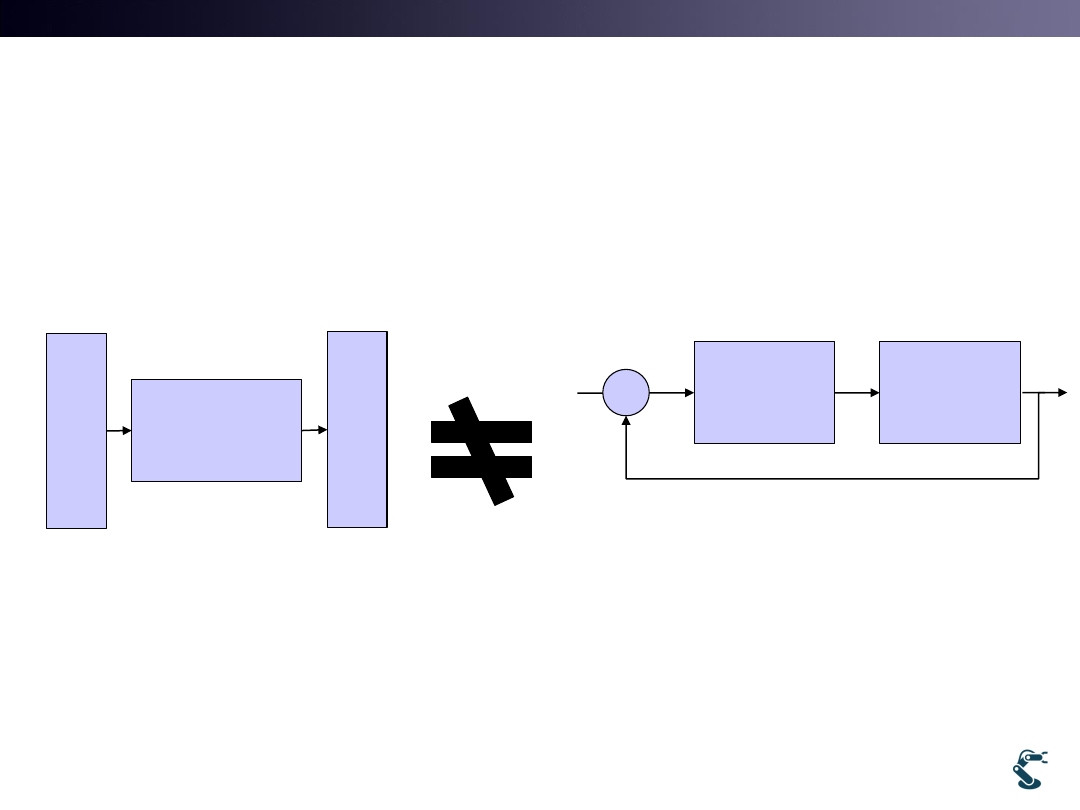
4. It is different with Function Estimation.
It tries to learn Dynamic System.
• Think Control Diagram
• Input and output are different in every time Failed
7
Neural
Network
x
y
Data (x, y) are given
Goal is to find the proper
function, NN
( )
y
f x
Learning the function!
Learning
method
NN
System
xd
e
T
Data ‘e’ are given, but ‘T’ are NOT.
Goal is to find the NN that makes x to be xd.
Eg. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
Tries to solve System Dynamics.
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
How do Learning this case?
8
• Something is different with Neural Network…

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Learning Goal is “to learn a Process”
• Process is a series of sequential events.
• Design issues
– We can make a process like a instant data
– Each dot in a space is a process Learning a process
– Every dots in a space are a non process but an image.
• How to learn a process?
– There are two types of popular methods.
– 1. Recurrent Neural Network, RNN
– 2. Reinforcement Learning, RL
– (3. Classifier Hidden Markov Model, HMM)
9
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Types of Learning methods
• Learning Function
• Learning Dynamics (or Sequences)
10
X
Sample
Learning
Module
Y
,
( )
( )
NN learns
Y
NN X
f X
Learning
Module
k
x
1
k
x
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
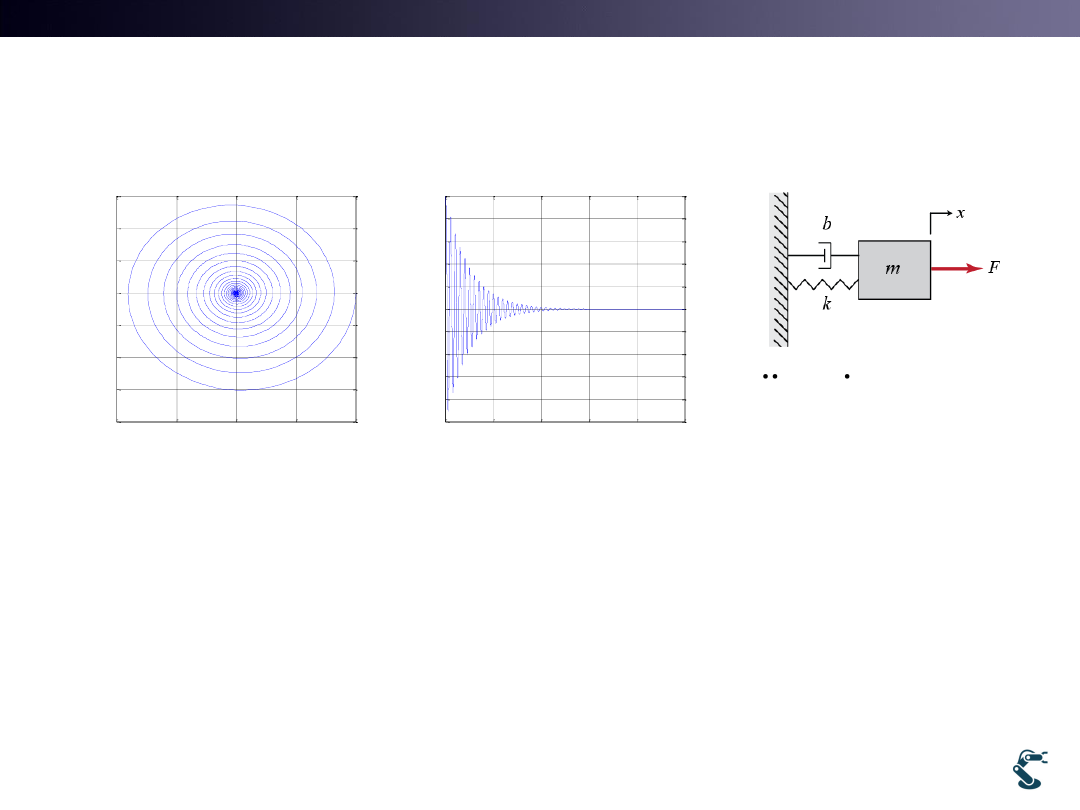
How to learn Dynamics or Sequences
• 1. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
• 2. Recursive Neural Network (Becoming Perished)
• 3. Reinforcement Learning
– However, it has some different features(Stochastic)
11
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
x
xd
state space
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
time(ms)
x
(t
)
( )
mx cx kx
F t
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
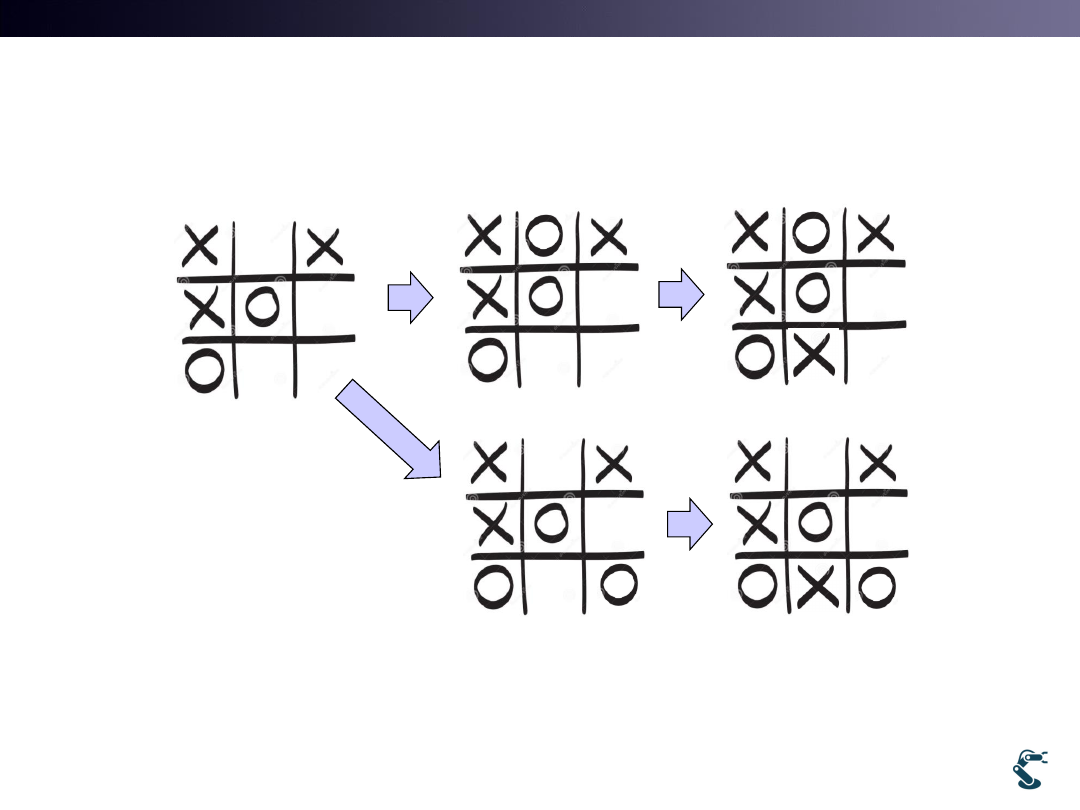
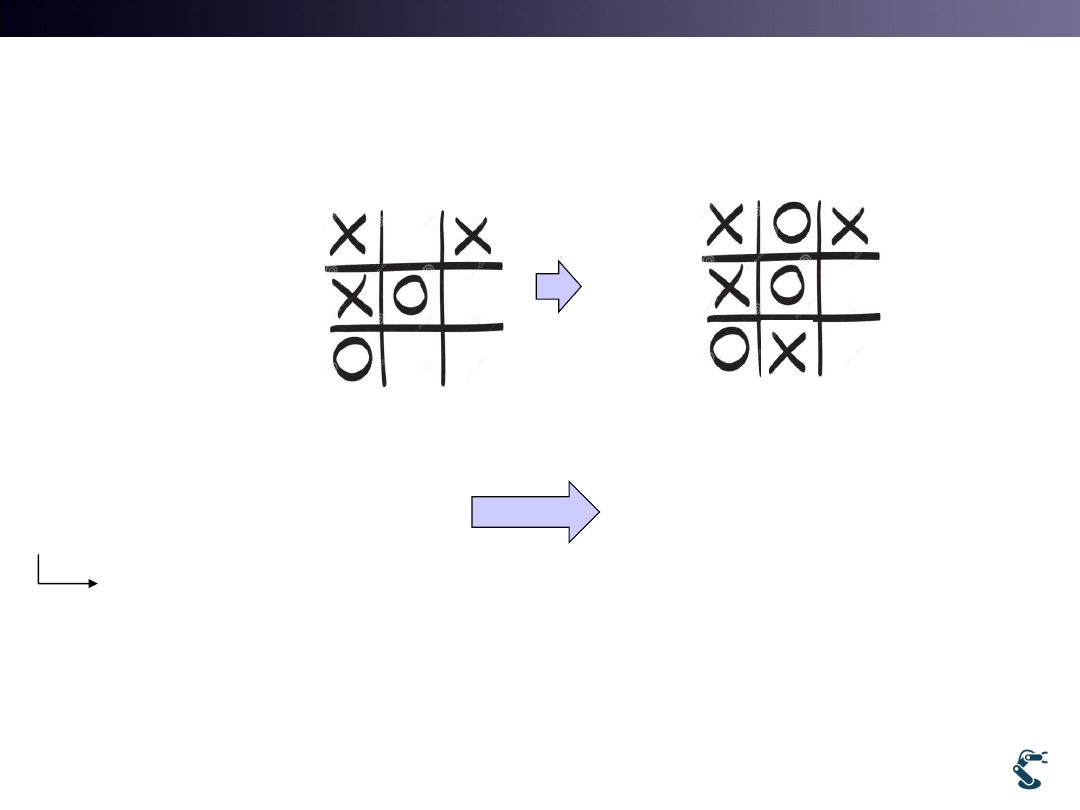
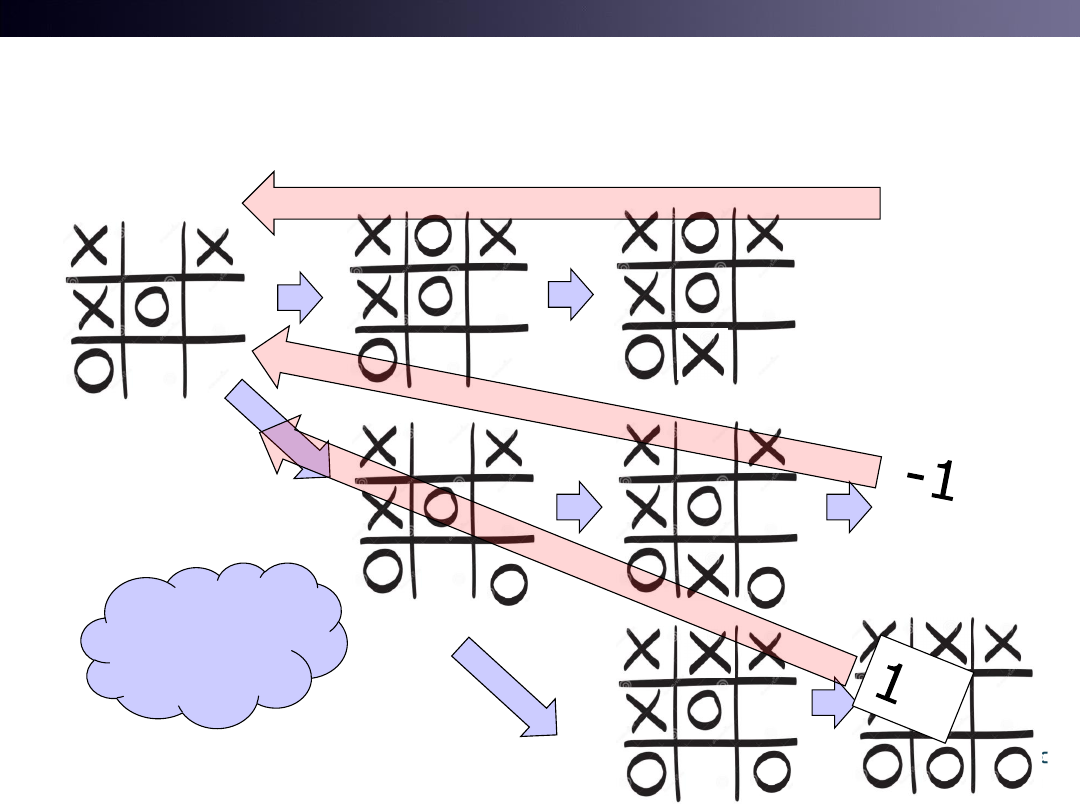
Remind Tic-Tac-Toe
• Question 1: What is a state vector in Tic-Tac-Toe?
• Question 2: What is an input and an output?
– There are No Input and Output
– There are only States and Actions
12
k
x
1
k
x
[ , ,
,
, , , , , ]
T
k
x
X
X X O
O
1
[ , ,
,
, , , , X, ]
T
k
x
X O X X O
O
[ , ,
,
, ,
O
, , , ]
T
k
x
X
X X O
O
Action
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Input / Output is Similar to Control
13
Learning
Module
k
x
1
k
x
Learning
Module
k
u
1
k
x
( )
mx cx kx
u t
0
mx cx kx
0
k
u
k
x
( , )
X
f X t
( , , )
X
f X u t
:
0
k
case u
Environment
1
k
k
x
x
:
0
k
case u
T&C LAB-AI
What we Minimize?
2
14
Or What we Maximize?
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Local and Global Goal
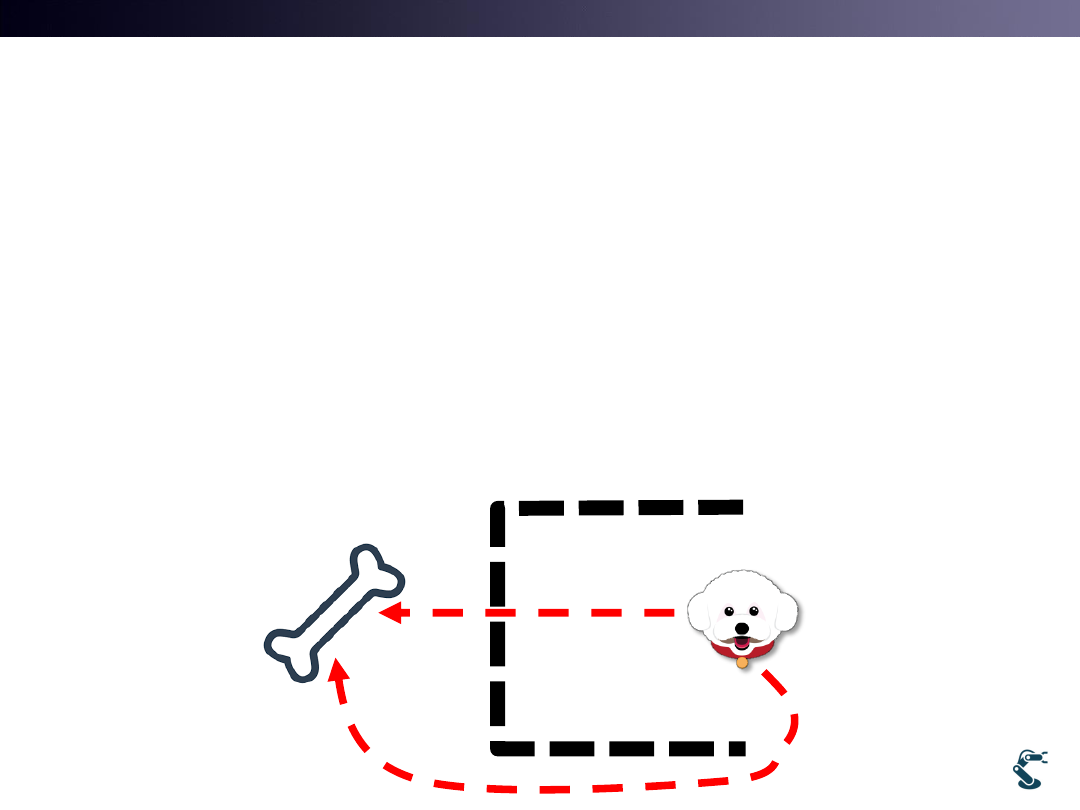
• Minimize error is the strong issue in Learning Method
– In other words, Optimization is the Learning.
• Local Goal
– A dog tries to follow a bone But failed
• Global Goal ( Nearly Global Optimization)
– A dog tries to avoid obstacles locally weak but globally success
15
Local Goal
Global Goal

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
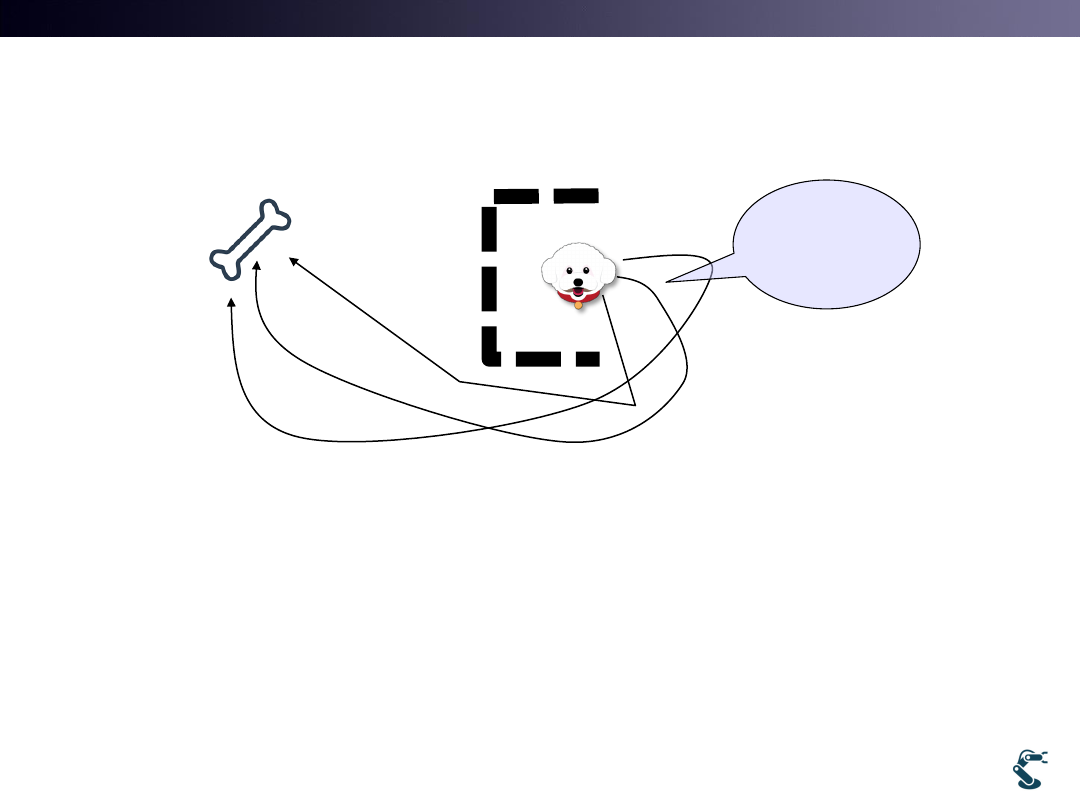
Example
• Learning is achieved by several trials.
• 1st turn : follow the local goal, but get the goal
eventually.
• 2nd turn: unsure but a dog remembers the solution
• 3rd turn: Fully being learned.
16
Try to follow the local goal
It is Not sure, but finally
get the goal
Absolutely, success!
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
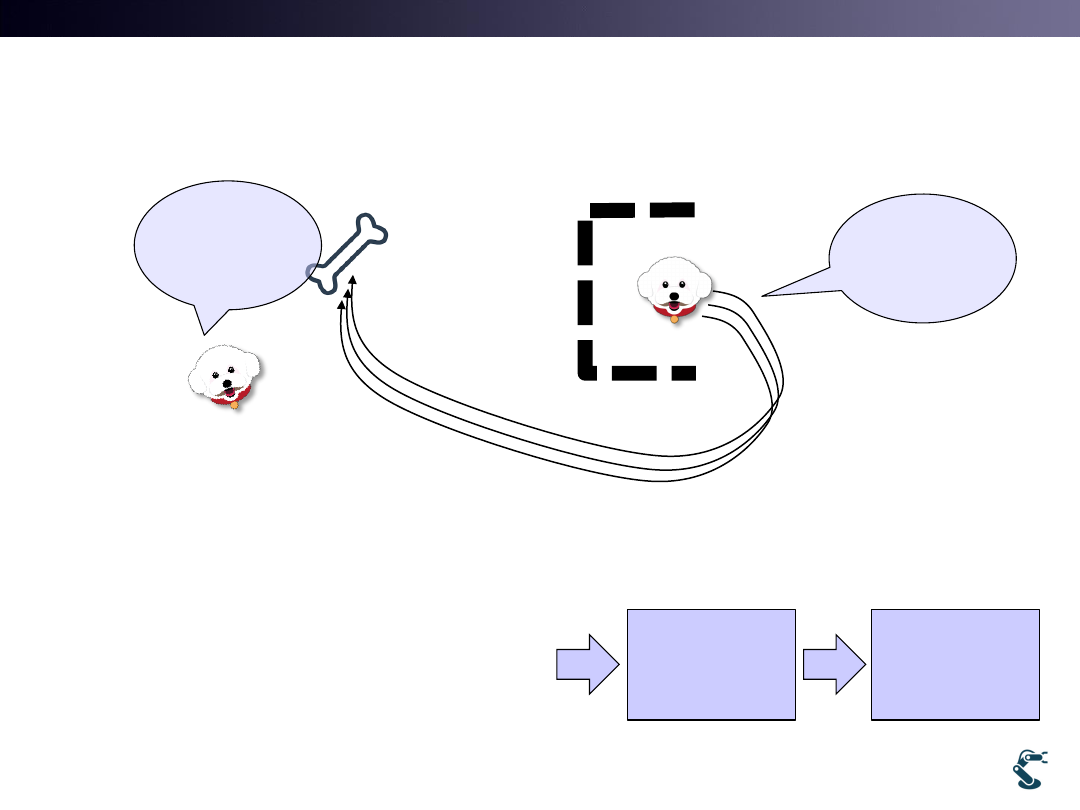
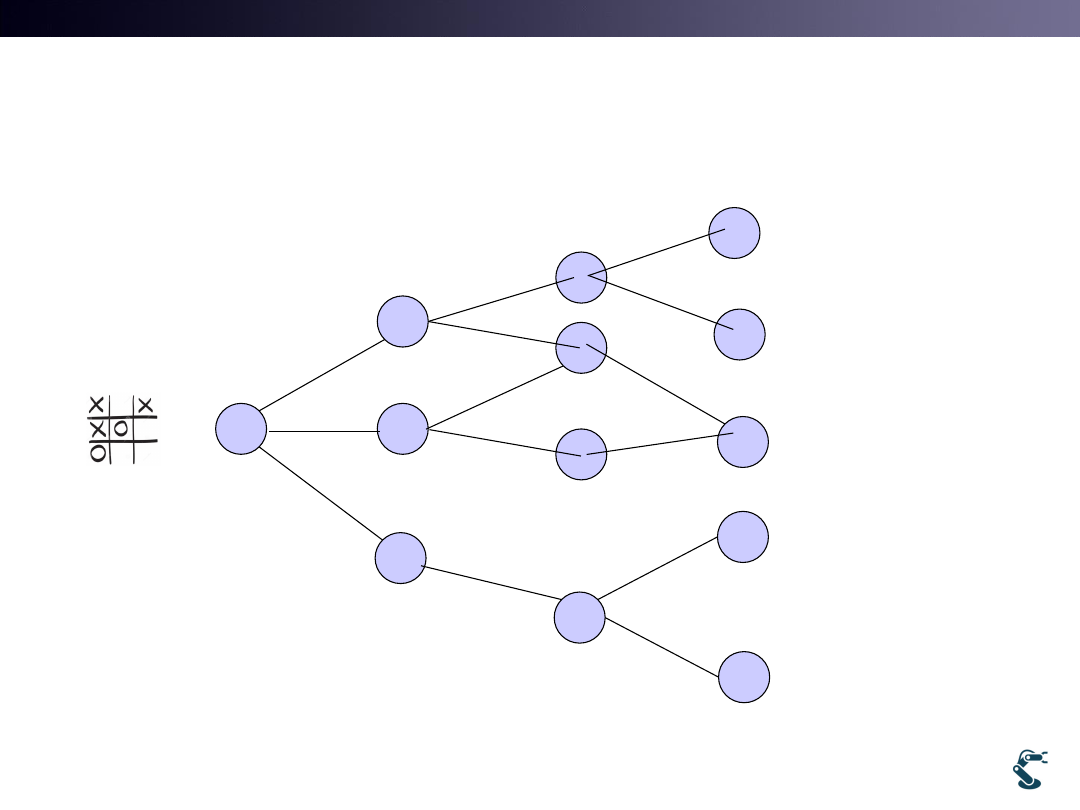
Issue. 1. There are so Many, Many Paths.
• Step 1. Each path must be scored
• Step 2. I might find the best one.
• Step 3. But, I did not pass the best one Try it again.
• Step 4. Finally Find the Best One.
17
Which one
is the optimal?
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
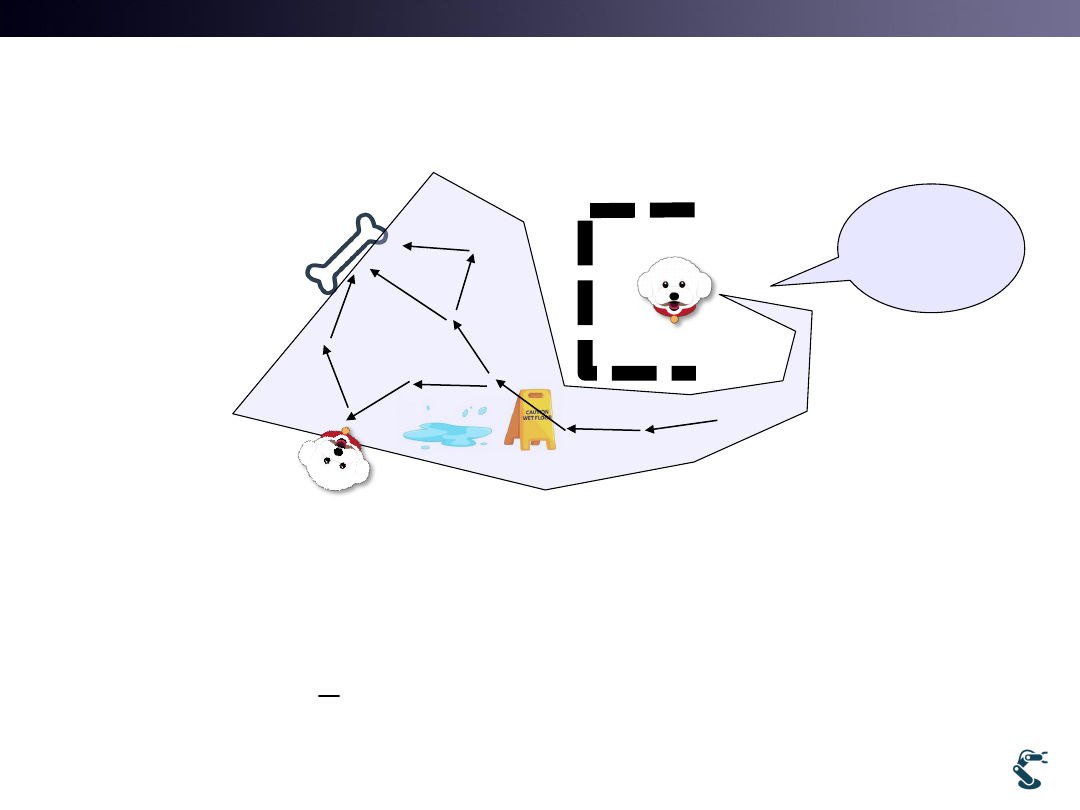
Issue. 2. Stochastic Problem
• An agent follows the same path.
• But Scoring is not Accurate.
– 1st turn: the score was 1.
– 2nd turn: the score was 1.2
– 3rd turn: the score was 0.9
18
I believe
I can get
The score, 1!!
Environment
Is not equal.
Use
Stochastic
(Probabilistic)
Approaches
Scores
are not equal.
Why?
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Issue. 3. Expectation of ALL Cases
• Expectation is the terminology in Probability
• Every events are considered as Probabilistic cases.
Probably,
I expect
1.12 score!!
1
{ } lim
( ), is PDF, Not Probability
n
i
i
i
n
i
i
E R
R
R p R
p
n

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Expectation in Probability
• Expectation is the value that is weighted by probability
• Expectation of rolling a dice.
20
( )
( )
, ( ) is the Probabilistic Density Function
( )
( ), ( ) is the Probabilistic Mass Function
i
i
i
E x
xp x dx p x
E x
x p x
p x
6
6
6
Prob. (
)
( )
1
1
1
1
{ }
p( )
P(
)
1
2
,... 6
3.5
6
6
6
6
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
P x
x
p x
E x
x
x
x
x
x
x
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
RL uses Return Value(Scores) in Future..
21
Draw!
Many cases occur.
What is the higher
Return?
0
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Scoring on every transition
22
1
5
-3
0
1
3
How we summarize everything?
T&C LAB-AI
Stochastic Environment
3
23

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Everything is Stochastically Determined
: Stochastic(Probabilistic) World
• Think the example
• Initial(Start) position: an agent starts its exploration.
• Terminal position: an agent ends its exploration.
• Which way (Left or Right) is better ?
– You answer the right turn.
– Why? How can you teach it to an agent
24
Start
Reward: +1
Terminal
Terminal
Reward: +2
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
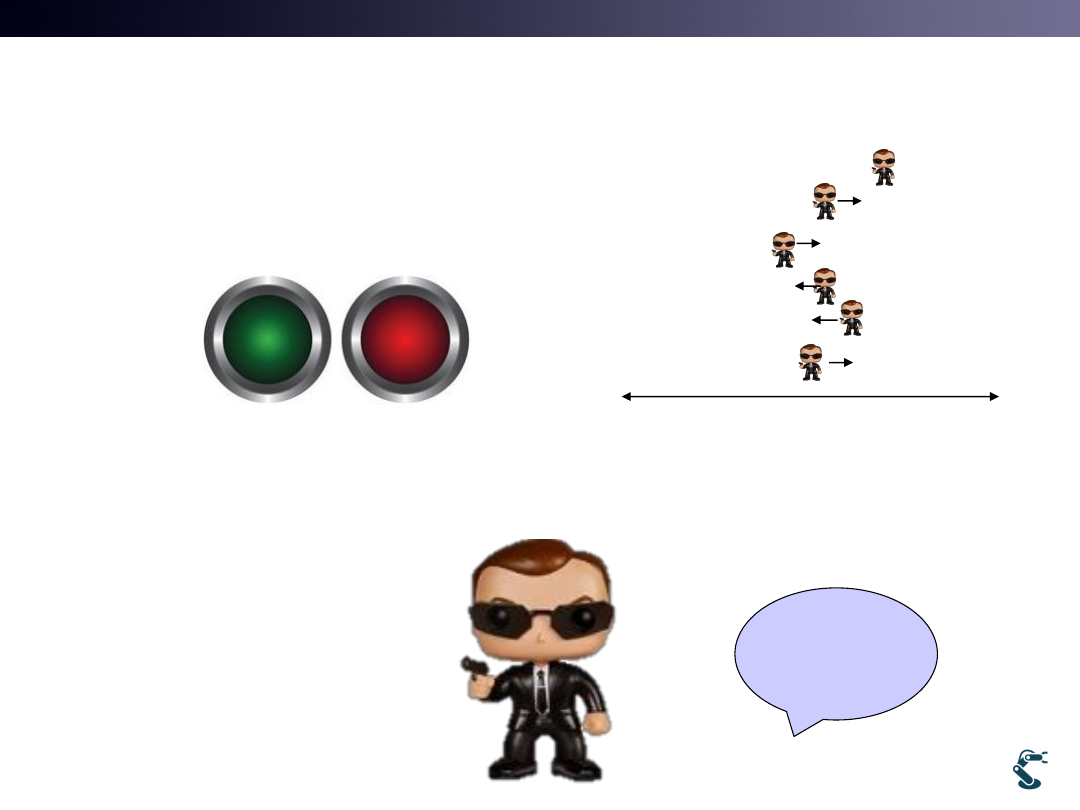
Our Agent has No Information
• An agent has two buttons
• When an agent finish its exploration, it gets a Reward.
• “An agent is blind”
25
Agent
moves
randomly
Agent does NOT know which button is left or right
How it works?
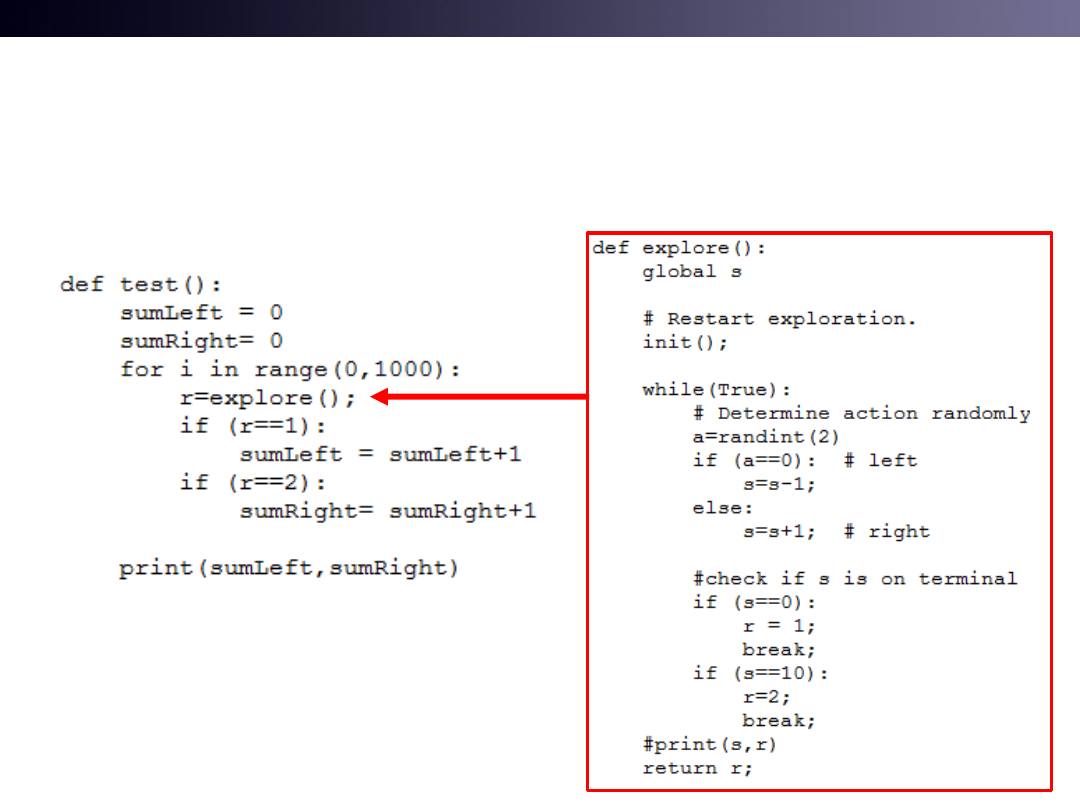
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Do 1000 Explorations
• Run l9test1.py
26

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Result is ..
Result Sum of
Left
goals
Sum of
Right
goals
1
506
494
2
485
515
3
518
482
4
498
502
5
503
497
6
517
483
7
485
515
27
What the…!
No Meaning!!
• It is just Left or Right example.
• If we do many iterations, left becomes equal to right.
– Ex) left 500 , right 500, Probability is 0.5

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
What we Learn from this STUPID Example
• 1. if we push Red or Green button “Randomly”,
– We can go left or right terminal
– Thus, probability of Left and Right is
• 2. However, we know that “Right” will get better reward
– How can we express this?
28
(
)
0.5 (
)
0.5
p left
p right
(
)
(
)
1
1
1
2
1.5
2
2
left
right
r p left
r
p right
At an initial state, we expect that
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Sum of Rewards is Good for Learning
29
Initial state
Reward: +1
Left
Terminal
Right
Terminal
Reward: +2
Left Terminal
Right Terminal
Number of cases
503
497
Sum of Reward
503
994
average
503/503=1.0
994/497=2.0
Avg
= 1
Avg
= 2
Finally, I can say that Average of
Reward at the RIGHT is better!
Run l9test2.py

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Well, World is not so easy…
• If it is a tough road, an agent receives -0.1 reward.
– There are some Monsters as in video games.
• In each Movement, reward is -0.1…
– Which way is better?
30
Initial state
Reward: +1
Terminal
Terminal
Reward: +2
Distance=3
Distance=7
Damage
-0.1
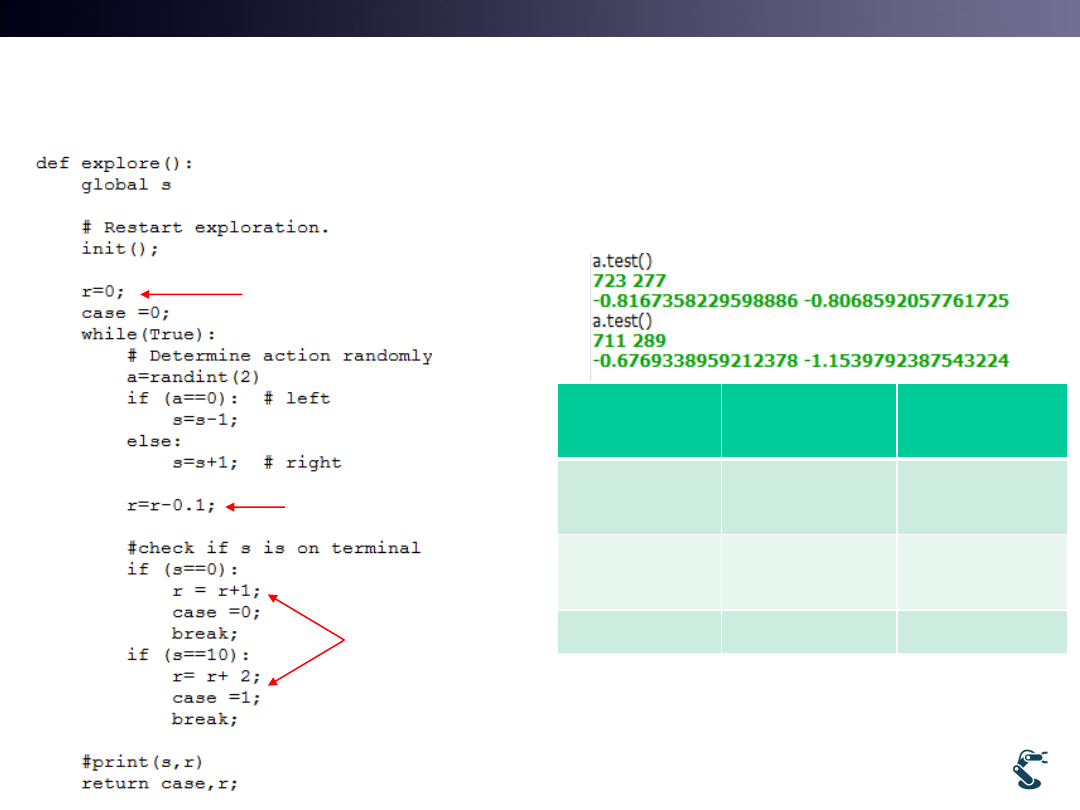
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
See l9test3.py
• How it works?
31
Initial reward
Monster attack
Final reward at
each terminal
Left
Terminal
Right
Terminal
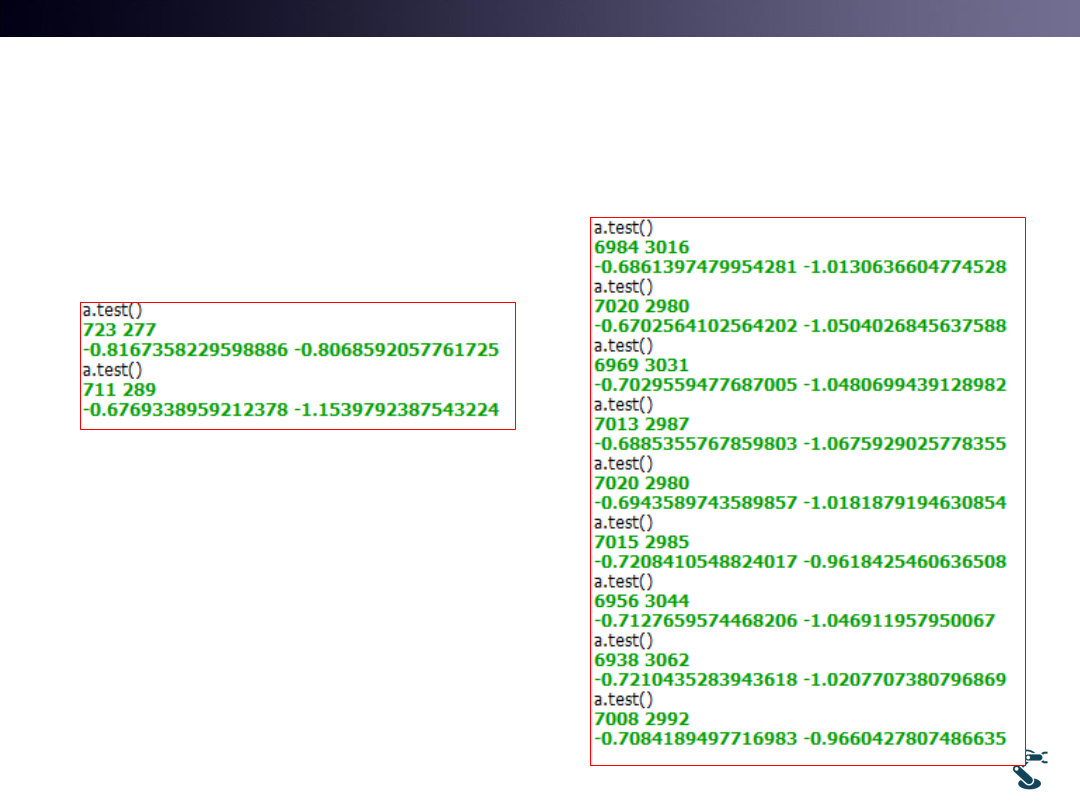
1st test
723
Avg= -0.817
277
Avg=-0.807
2nd test
711
Avg= -0.677
289
Avg=-1.154
Which one is better?
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
l9test3.py Test
1000 10000 times.
• Which one is better?
• With 10000 tests,
“Left” is better.
32
1000 times
10000 times
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
See the Result, Carefully
• Optimal might be
– Left Distance is 3 and
Left reward is 1.
1 -3*0.1 = 0.7.
– Right Distance is 7 and
Right reward is 2.
Then, 2- 7*0.1 = 1.3??
• Why Avg. left and right
is so different?
33
It is a stochastic world.
An Random agent CANNOT reach
at Right Terminal within 7 steps.
(Probably Not)
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Extend This Concept
• Sum is Good?
– Case 1) s=[ 3, 2, 1, 0] Sum of rewards= 1-3*0.1=0.7 (Best)
– Case 2) s=[ 3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,3,2,1,0] Sum =
1-19*0.1 = -0.9
• Average is Good?
– Case 1) 3 turns 0.7/3 = 0.233
– Case 2) 19 turns -0.9/19= -0.047
34
Initial state
Reward: +1
Terminal
Terminal
Reward: +2
Distance=3
Distance=7
Damage
-0.1

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Summary
• Average of all rewards
– Meaningless [3,2,3,2,3,2…. ] only reduces average rewards.
– Increasing average of all rewards is to find the optimal path
• Why Not Sum?
– Summation is just a Cost function in deterministic ways
• Why Average?
– Average is an alternative expression of Expectation
– Our problem is in a stochastic world Use Probabilistic method
35
k
k
R
J
r
1
{ }
k
k
R
r
E R
N
: max(E{R})
optimal path